Abstract
Background: Post-transplant high dose cyclophosphamide (PT-CY) effectively prevents graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). However, the use of PT-CY in HLA-identical HSCT is less explored. In this study, we analyzed the results of PT-CY as GVHD prophylaxis in HLA-identical sibling HSCT and compared them with those obtained after prophylaxis with methotrexate (MTX) plus cyclosporine (CsA).
Methods: 107 HLA-identical sibling (10/10) HSCT from 2 Spanish centers have been analyzed: 50 performed consecutively between 2010 and 2015 using MTX-CsA as GVHD prophylaxis, and 57 performed consecutively between 2014 and 2018 using PT-CY.
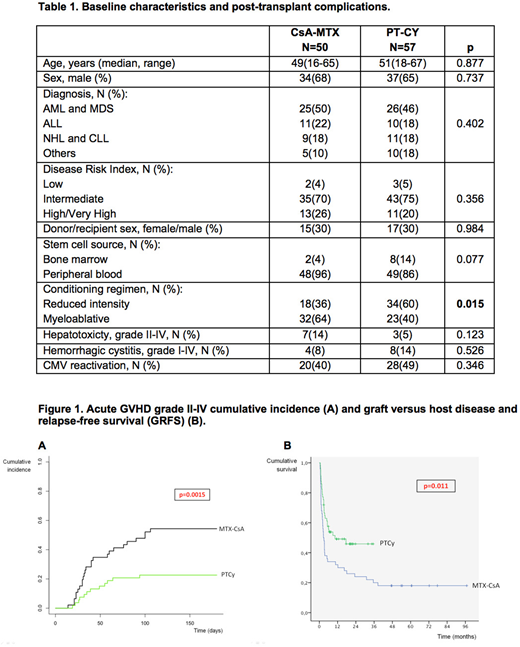
Results: Baseline characteristics and post-transplant complications are shown in Table 1. GVHD prophylaxis consisted in MTX days +1, +3, +6 and +11, and CsA from day -1 in the MTX-CsA group. The PT-CY group received cyclophosphamide 50 mg/kg/d on days +3 and +5 in 38 patients (65%), combined with CsA from day +5, and cyclophosphamide on days +3 and +4 in 19 patients (35%), followed by CsA and mycophenolate mofetil from day +5. Graft source was PBSC in 96% in the MTX-CsA group and 86% in the PT-CY group. Conditioning regimen was myeloablative in 64% and 40%, respectively. Neutrophil and platelet engraftment was significantly delayed in the PT-CY group (14.5 (11-27) vs 15.5 (13-37), p=0.02; 11.5 (8-180) vs 20.5 (10-43), p=0.02). After a median follow-up of 60 months for the MTX-CsA group and 15 months for the PT-CY group, 2-year overall survival (OS) was 56% (42-70) and 78% (67-90) (p=0.088), and event-free survival (EFS) was 48% (34-62) and 62.5% (42.5-82.5) (p=0.054), respectively. Cumulative incidence at 100 days of grade II-IV (52.2% vs. 22.6%, p=0.0015), and III-IV (24.4% vs. 8.8%, p=0.016) acute GVHD were significantly higher in the MTX-CsA group (Figure 1A). No differences were observed in the 2-year cumulative incidence of chronic moderate to severe GVHD (26% vs. 16.7% (p=0.306)). No differences were observed in the 2-years cumulative incidence of relapse (27% vs. 28% (p=0.47)). Non-relapse mortality (NRM) at 2-years showed a higher trend in the MTX-CsA cohort (24% vs. 8.8%, p=0.054). Finally, the composite endpoint of GVHD and relapse-free survival (GRFS) at 2-years was significantly better in the PT-CY group (48% vs. 24%, p=0.011) (Figure 1B).
Conclusions: In our experience, GVHD prophylaxis using PT-CY combined with additional immunosuppression after HLA-identical sibling HSCT, using mostly peripheral blood as graft source, reduced the cumulative incidence of acute GVHD compared to standard prophylaxis with MTX-CsA, leading to an impact on GRFS. To our knowledge, this is the largest comparative retrospective cohort reported. Further prospective studies with longer follow-up are needed to confirm these observations.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal